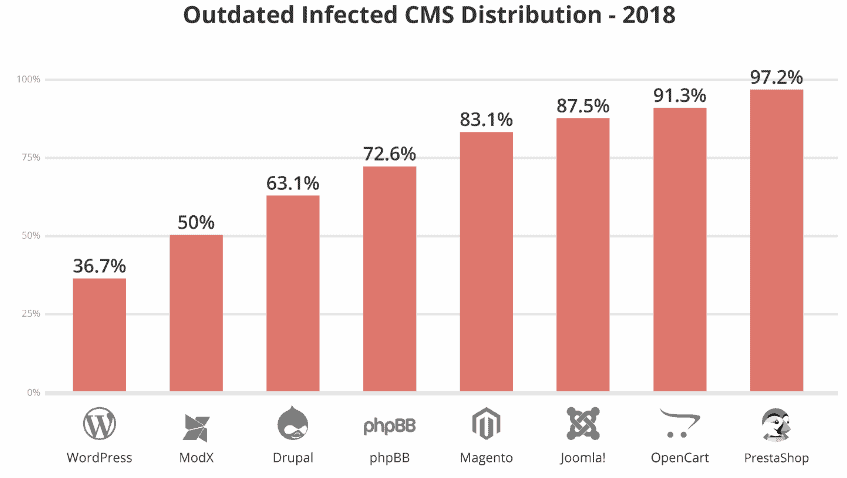
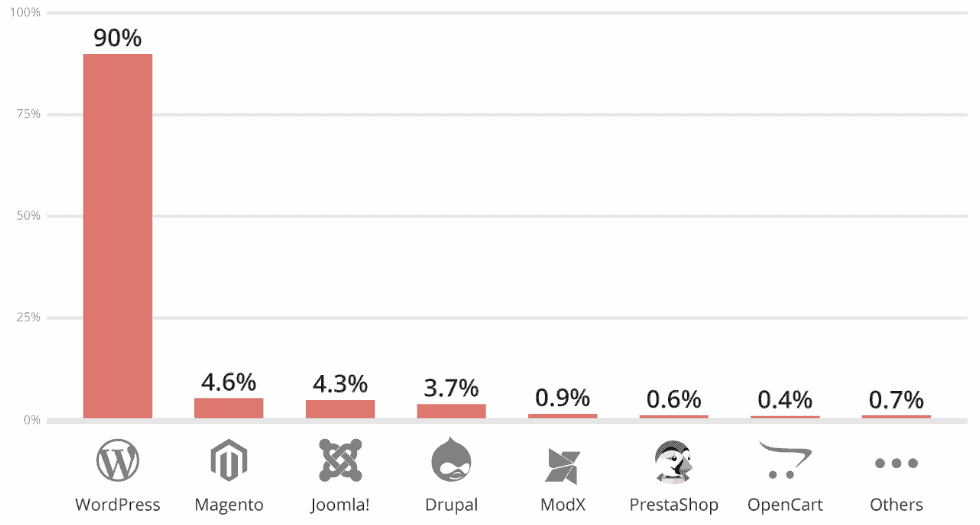
Approximately 90% of all hacked content management systems (CMSs) were WordPress sites that Sucuri investigated and helped fix in 2018. Magento (4.6 %), Joomla (4.3 %), and Drupal (3.7 %) came in a distant second, third, and fourth, according to a report published yesterday by the company. Sucuri experts blamed most hacks on plugin and theme vulnerabilities, misconfiguration issues, and webmasters ‘ lack of maintenance, which often forgot to update their CMS, themes, and plugins. Experts said that when they were called in to remedy a hack, only 56 percent of the sites they investigated were running an up-to-date CMS. E-Commerce & Outdated Plugins But while WordPress accounted for 90 percent of all hacked sites, most of them were running up to date versions. Sucuri said that an outdated version was run by only 36 percent of the wordpress malware redirect hack investigated by the company.
Source: Sucuri On the other hand, when found to be hacked, CMSs like PrestaShop, OpenCart, Joomla (Joomla infected with malware fix it now), and Magento were running on an outdated version almost always. “This trend in outdated versions supports the idea that e-commerce sites are known to slow down on updates in order to avoid breaking functionality and losing money,” said Sucuri. “Attackers are highly interested in targeting e-commerce websites with valuable customer data (i.e., credit card and user information) and it is imperative that these website owners update their software to ensure that their websites have the latest security enhancements and vulnerability patches.” Yet, despite some sites running outdated CMS versions, “the leading cause of component vulnerability infections”.
Source: Sucuri SEO SPAM When the hacks occurred, Sucuri said hackers typically deployed backdoors, with the company finding one on 68 percent of all the sites under investigation. Sucuri experts said hackers also used about 56 percent of hacked sites to host malware for other operations, and deployed SEO spam pages to 51 percent of hacked sites — a number that has risen from 44 percent in 2017 over the past year. SEO spam] is one of the most rapidly growing families in the past years,” said Sucuri. “They are difficult to detect and have a strong economic engine driven by impression-based affiliate marketing.” Most often, SEOs occur with PHP, database injections or.taccess redirects because of the attacks of Search Engine Poisoning (SEP), in which attackers attempt to abuse site rankings to monetize affiliate marketing or other blackhat tactics. SEO-impacted sites are often spammed or redirect visitors to spam-specific pages. Unwanted contents are regularly reported in pharmaceutical ad placements but may include injected contents for other popular industries, such as fashion and entertainment (i.e. pornography, essays, fashion-brands, loans, and online gambling).